With most businesses taking their operations online, many processes are now conducted remotely.
That means companies are adjusting to new remote workflows from team communication to client-related activities.
Fortunately, technologies such as electronic signatures are available so enterprises can still continue their business as usual. Companies can continue processing contracts, agreements, and other legal documents that typically require signatures even when they are in a different location from their customers.
Before diving deeper into how to create a secure electronic signature, let’s start from the basics.
What is an Electronic Signature?
Whether you are self-employed or a multinational company with customers around the world, signatures are essential in solidifying business relationships.
At its simplest definition, an electronic signature, or e-signature, is the electronic form of one’s inked signature, which is attached to electronic documents.
Just like its older form, an e-signature represents a person and verifies his/her identity. It serves as proof of consent, endorsement, and contractual status outlined in the document where it is attached.
Different countries have varying definitions of e-signatures if one exists in their law.
For example, the United States defines e-signatures under the Electronic Signature & Records Association (ESRA) as any electronic symbol, sound, or process that is associated with a record and executed by a person with the intent to sign the said record.
Most countries adopt this versatile definition of e-signature. That means it extends beyond its traditional written form.
For instance, by legal definition, the act of purchasing digital goods from Amazon is a form of electronic signature. This is why receipts or proof of purchase are legally valid even without your written signature.
How to Create a Secure Electronic Signature?
There are three primary ways to create an electronic signature, each with varying security levels.
Simple Electronic Signature
Signing a hard copy of a document and scanning it is an example of a simple electronic signature.
Others use apps to directly sign electronic documents. For instance, you can try the Wisestamp signature maker.
(Image source: wisestamp.com)
Sending it using an email account verifies your identity, which binds the signature to the document.
Similarly, associating a username and password to a digital record or accepting a terms and conditions document are considered simple signatures.
The logical association between the signature and the signing entity, i.e., the email address, links the two together. However, it does not provide any legal identification of the signer.
That means a simple e-signature only provides the lowest security level.
Advanced Electronic Signature
An advanced electronic signature (AeS) needs to meet specific requirements, such as:
You need to use standards-based e-signature services through a provider to create an advanced e-signature.
Look for Electronic Identification, Authentication, and Trust Services (elDAS) compliant providers that serve transactions under the European Single Market.
Similarly, the United States follows the Digital Signature Standard (DSS) under the Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS).
Qualified Electronic Signature
A qualified electronic signature (QES) also follows the standards for advanced electronic signature with additional requirements:
E-signatures created through electronic National Identity Documents are examples of qualified electronic signatures.
That means national eID cards, ePassports (ePP), and other similar documents where your identity, such as biometrics, are collected and stored using a qualified electronic signature.
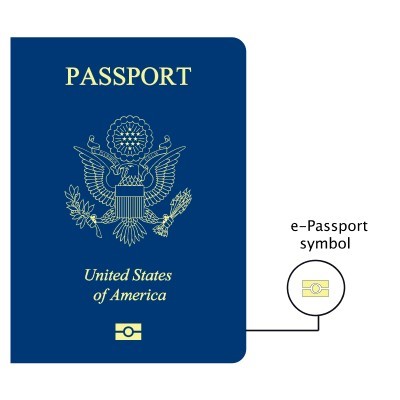
(Image source: travel.state.gov)
As such, it provides the highest level of security for e-signatures.
Are Electronic Signatures Legal?
While there are numerous standards and protocols in validating e-signatures, their application and legal viability differ in each country. Here are some examples.
The United States
The U.S.’ ESIGN Act of 2000 outlines the adoption of e-signatures in various business processes, transactions, and relationships.
As mentioned, the law recognizes any electronic symbol, sound, or process that is logically associated with a record or a document.
It ensures that e-signatures are valid as evidence in the court of law. Additionally, it declares that e-signatures are equal to and can substitute ink or wet signatures.
Consequently, it protects the validity, enforceability, and effect of electronic documents.
European Union
eIDAS, aside from outlining standards and protocols, also states that any form of e-signature is valid as long as the parties involved in the transaction, process, or agreement consent to the use of such electronic signature.
China
Initially, the Electronic Signature Law of the People’s Republic of China, later amended as E-Signature Law, recognizes the validity of e-signatures for civil contracts.
However, they are not valid for marriage licenses, adoption papers, inheritance records, real-estate contracts, and public utility suspensions.
India
India’s Information Technology Act also recognizes the validity and applicability of e-signatures in most business applications and transactions.
However, electronic signatures are not recognized in real estate deals, power of attorney contracts, and wills.
Note that the country indicates that digital signatures, not e-signatures, are legally equal to wet signatures.
Canada
The Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act in Canada outlines that e-signatures are legally valid and equal to ink signatures.
Just like India, e-signatures are not valid for real estate contracts, power of attorney documentation, and wills.
Electronic vs. Digital Signatures: What’s the Difference?
While they may sound interchangeable, electronic and digital signatures are different from each other.
The following factors characterize electronic signatures:
On the other hand, digital signatures have the following qualities:
Conclusion
Without e-signatures, it will be difficult to conduct international business. Imagine sending printed documents overseas? Or faxing a copy of contracts?
Furthermore, as businesses continue to shift to fully online operations, e-signatures along with digital signatures, continue the purpose of traditional ink signatures, especially in contracts, agreements, and similar documents.
As technology improves, expect to see highly secure and private versions of electronic signatures in the future.